

Encourage the client to void every 2 hours.These are essential in promoting the strength that the mother would need during delivery. Some interventions are implemented to give comfort and safety for the mother during and after the labor period. If there is episiotomy performed, perineal repair should be integrated into the care plan.Once the placenta is delivered, oxytocin should be administered intramuscularly to promote uterine contractions. Placental delivery should be given focus at this stage.Perineal cleaning is also an integral part of the second stage.Ĭare of the woman in the third stage of labor.Another important part is the promotion of second stage effective pushing.The position of birth wherein the woman is most comfortable must also be determined at this stage.During the second stage of labor, the place of delivery of the woman must be prepared.Upon delivery of the newborn, mother and child should be given unlimited opportunity for breastfeeding and bonding.Ĭare of a woman in the second stage of labor.Allow the woman to assume a non- supine position for delivery.Artificial interventions should also be prohibited. The woman must also be allowed to move freely throughout the labor.Labor should be allowed to start naturally, not artificially induced.With all the data gathered during assessment and through an accurate diagnosis, a care plan for the woman in labor would be made to aid her through her progress.Ĭare of a woman in the first stage of labor The signs of placental expulsion are lengthening of the umbilical cord, sudden gush of vaginal blood, changes in the shape of the uterus and its firm contraction, and the appearance of the placenta at the vaginal opening.The third stage begins with the birth of the infant until the delivery of the placenta.Crowning or the appearance of the fetal head on the vaginal opening occurs.The woman may experience an uncontrollable urge to push and bear down with every contraction.
#CARDINAL MOVEMENTS OF LABOR FULL#
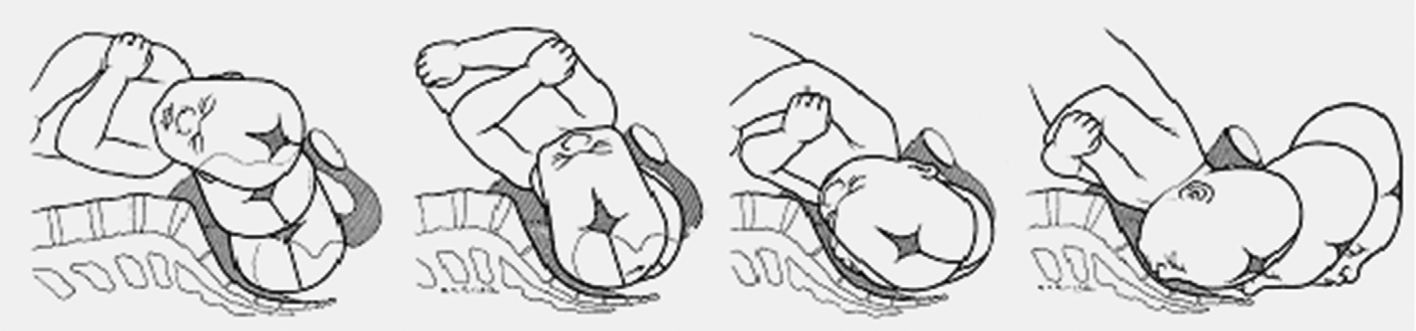
Effacement is the shortening and thinning of the cervical canal. Assess for the effacement and dilatation of the cervix.Station is the relationship of the presenting part to the level of the ischial spines. Engagement refers to the settling of the presenting part into the pelvis at the level of the ischial spines. Assess for the engagement of the fetal head.This is the scanty or sudden gush of clear fluid from the vagina. Assess for the appearance of show, which is blood mixed with mucus and would be present once the operculum or mucus plug is expelled.The signs of true labor are contractions that begin irregularly but progresses regularly and predictably, the pain is felt first at the lower back and circles towards the abdomen, continues to progress no matter what the woman’s activity level is, increases in duration, frequency, and intensity and cervical dilation is already present. The woman would be placed under observation during labor to monitor her progress and ensure a safe delivery for her and the child. The key to a successful individualized care plan is the precise assessment and accurate obtaining of data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
